پاویون انرژی لندن
معمار: امیر آرمانی اصل، خشایار محمدی
موقعیت: لندن، انگلستان
تاریخ: 1394
مساحت: 80 مترمربع
وضعیت: طرح پیشنهادی مسابقه / طرح برگزیده
کارفرما: ArchTriumph
همکار طراحی: رضا پولادوند
در مسیر دستیابی به ایدههای شکلگیری این پروژه، به نمود خود کلمه انرژی در طراحی فکر کردیم و در نتیجه، انرژی را به زبان انتزاعی و در مرحله بعد، با در نظر گرفتن زمینه سایت و دریافت رفتار انسانها در سایت پروژه (غرب لندن) پیش بردیم. نمودهای محیطی جذابی در این منطقه وجود داشت؛ از آنجا که این پاویون در بین یک موزه دوران کودکی و کلیسا قرار داشت و سایت پروژه پر از انرژیهای مختلف بود و نیز از آنجا که پروژه قرار بود در ماه تابستان، در محل مشخصشده ساخته شود، با توجه به نوع استفادهای که قرار بود عموم مردم در محدوده پاویون داشته باشند، از جمله برگزاری فستیوالهای تابستانی برای کودکان، مسیر فکری ما به سمت موضوع تعامل رفت. تعامل واژهای مهم در طراحی این پاویون است، زیرا زمانی این پاویون، پاویون انرژی نامیده میشود که سایت پروژه / انسان / پاویون در کنار هم، به خوانایی این فضا کمک کنند و یک تجربه فضایی منحصربهفرد را ارائه دهند.
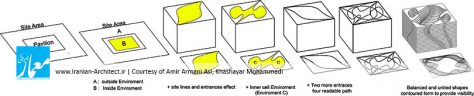
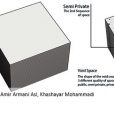
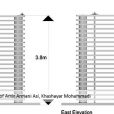
ایده پاویون به خاطر داشتن خوانش فضایی بالا، از یک مکعب ساده شروع شد و ما با در نظر گرفتن یک نظم سازماندهیشده، به یک ساختار زمانمند رسیدیم، به این صورت که با توجه به اینکه نقاط شاخصی در سایت، از نظر دیدهشدن پروژه برای ما مهم بود، به یک کیفیت فضایی متفاوت و شاخصه آن فکر کردیم تا افرادی که در بیرون قرار دارند و افرادی که در داخل پاویون قرار میگیرند، به این کیفیت فضایی دسترسی داشته باشند.
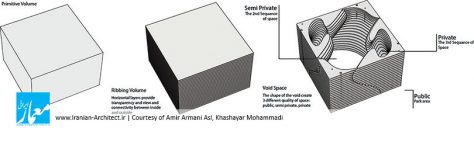
پاویون انرژی دارای سه کیفیت فضایی مختلف هست: یکی، فضایی که در اطراف پاویون در سایت وجود دارد که فضای عمومی معرفی شده و دومین فضا، مابین هر جزء تشکیلدهنده پاویون هست که فضای نیمهخصوصی معرفی شده است و سومین کیفیت فضایی که افراد میتوانند در آن یک تجربه منحصربهفرد داشته باشند، فضای داخلی هر جزء است که فضای خصوصی است.
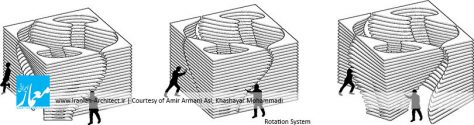
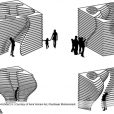
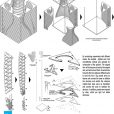
شاخصه اصلی در طراحی هندسه پاویون، توجه به انرژی و رفتار انسانها بود، به این صورت که برای واردشدن به این پاویون، باید با کمک دست، به پنلها فشار وارد کرد و با طراحی که در سیستم حرکت این پاویون انجام شده، با سیستم توئیست شکل با زاویه چرخش 30 درجه، میتوان وارد پاویون شد. چالش اساسی برای عملیشدن این ایده، سبککردن پنلهای تشکیلدهنده آن بود و برای این موضوع، ما با استفاده از یک فریم سبکوزن از چوب و پارچه، یک ایده را از بادبادک گرفتیم و از آنجا که این پاویون قرار بود در طی 3 ماه به روی عموم باز و قابل حمل باشد و با توجه به هزینه اجرایی کمی که از سوی کارفرما تعیین شده بود، با این ایده توانستیم در مدل فیزیکی که در مقیاس کوچکشده ساختیم، با این مسائل در ساخت کنار بیاییم و این پاویون را اجرایی کنیم.

برای بیشترکردن جذابیت این پروژه، ما به دو موضوع مهم، یعنی شفافیت و نیمهشفافیت فکر کردیم که برای پاسخ به این موضوع، به پر و خالی کردن بین صفحات تشکیلدهنده هر جزء اشاره کردیم که همین موضوع، با شناخت یک نکته دیگر، یعنی فضای باز و بسته انجام شد، به این صورت که با چرخش صفحات، فضاهای مفیدی با ویژگی سایهاندازی و برای استراحت در خارج پاویون ایجاد میشود.
London Energy Pavilion
Architect: Amir Armani Asl, Khashayar Mohammadi
Location: London, United Kingdom
Date: 2015
Area: 80 sqm
Status: Competition Proposal / Triumph Mention
Client: ArchTriumph
Design Associate: Reza Pooladvand
Performative Twist Box
Energy can be defined and analyzed in different ways. However, it was tried to define the energy with an abstract view in this project. Energy is known to everyone given its usual encounter in everyday life. Walking, running, talking, playing and every other moment of life is a continuous stream of the energy conversion and consumption. Therefore, it can be concluded that human is a symbol of energy itself.
It is important to know how the energy can appear in an architectural space, especially a pavilion. A pavilion located in a lively place beside the childhood Museum with audiences familiar with various annual events that take every opportunity to walk, run, play and generally enjoy the environment and consume energy. How the pavilion can be a symbol of energy? Simply, by “People”. The more people run, play, sit, relax, come together to make a change and explore the space, the more energy will be released to the space; the more the people, the more the activity, the more the energy.
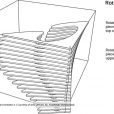
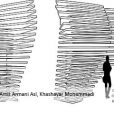
Therefore, it was tried to design the space so that to attract as much audiences as possible and provide a suitable environment to encourage them for more activity and exploration. Therefore, the pavilion is completely like a layered cube form from the outside with some embedded spaces to be explored by the audience. Layered form of the pavilion is considered for the readability purposes to provide an outside to inside view and vice versa. Entrance to the inside space can be a symbol of energy. Pavilion entrances were designed to be dynamic and were created by moving the cube body. They were located on four sides of the cube and created eight different modes of entry and unlimited varied forms. Number, direction of rotation and path of the entrances were selected so that to be readable and visible from all around to attract more audiences.
In addition, the pavilion was located in the site with appropriate angles so that to ensure good visibility in all directions. In addition to playing the role of entrance, openings cause fluidity of the form and make the pavilion to take new shapes in every moment of the day. This could encourage passers-by to take their own part in formation of the environment and make changes to it. Every time someone tries to enter the pavilion space, its form should be changed that can be attractive for observers and passers-by and calls them to the space. In addition, a third space has been considered inside the interior of the pavilion. By standing in the space, the audience can sense and share the transformation of the cubic form from a closer distance.
In general, it was tried to design an architectural space that involve the audiences and encourage them for more activity and exploration. Meanwhile, social ties, rest points, places for standing, leaning, sitting, talking, and cooperating have been considered. At any moment, the audience could form the required space, lean into it, sit, and create the shadow and so on. Therefore, especial attention was paid to the relationship between human and space and vice versa. The form invokes the audience activity and responds to it so that leads to a new space, and the cycle goes on continuously. At the same time, the permanent relationship between the created space and the natural environment and vice versa has always been considered. Layered structure establishes the connection between inside and outside in every moment and continuous changes of the forms, like a curtain located downwind, gives a new form to the connection at any moment.
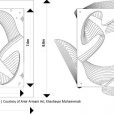
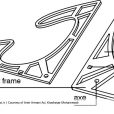
Framing Layout
By conducting experiments with different scales, the lightest and most cost-effective method was selected for construction of the pavilion. The original form of the structure is kept by the original axes, and moves around them. A second axis transmits the force between different parts to twist the form. Top panels serve as beams and connect the axes to stabilize the structure and restrict the structure rotation. In addition, panels were inspired by kites, which are light but stable structures.








تبریک فراوان . کار خیلی خوبیه
سپاس از نظرتون .ممنون